This page gives you a clear guide to the CAT4 Level E (Year 8) test, explaining the format, the skills it measures, and how each section works. You’ll find free sample questions covering all areas — verbal reasoning, non-verbal reasoning, quantitative reasoning, and spatial ability — plus a downloadable PDF with practice questions you can use offline or print.
Non-Verbal Battery
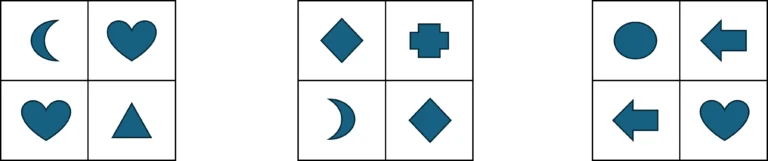
Figure Classification
In figure classification questions, you are presented with three figures on the top row that are similar in some way or share a certain characteristic. Then you need to choose the answer choice from the bottom row that also shares this characteristic. Please note that there can be more than one characteristic that binds the three figures in the top row together.
Explanation
The correct answer is (D).
The three figures on the top are similar in the following ways:
- They are squares that contain four smaller shapes (a heart, crescent, triangle, etc.).
- Two of the smaller shapes are identical and located diagonally to one another:
- Two hearts in the left figure.
- Two diamonds in the middle figure.
- Two arrows in the right figure.
Answer (D) is correct as it contains two identical circles that are located diagonally to one another.
Why are the rest of the answer choices incorrect?
Answer choice (A): It contains two identical shapes (hearts), but they are located next to each other vertically and not diagonally.
Answer choice (B): It contains only three shapes instead of four.
Answer choice (C): It contains three identical shapes (arcs) instead of just two. In addition, two arcs are next to each other vertically and not diagonally.
Answer choice (E): It contains four identical shapes (hearts) instead of just two.
Figure Matrices
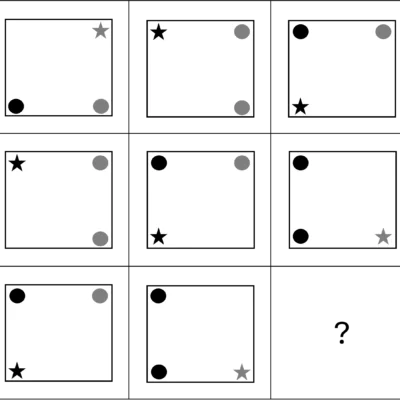
Explanation
The correct answer is (E).
This is a 3*3 matrix. In each frame there is a square that contains three inner shapes: one star and two circles. Note that these inner shapes are always located at the corners of the square.
Across the rows and down the columns, the rules are:
- Each time, each of the inner shapes (the star and the two circles) moves counterclockwise to the next corner of the square.
- When the inner shape is located on the right side of the square it is coloured grey.
- When the inner shape is located on the left side of the square it is coloured black.
Let’s apply these three rules on the last visible frame, to find the missing frame:
- The star should move to the top right corner and remain grey.
- The circle in the bottom left corner should move to the bottom right corner and turn grey.
- The circle in the top left corner should move to the bottom left corner and remain black.
Click here to see it visually.
Applying these rules brings you to answer choice (E)!
Verbal Battery
Verbal Classification
The three words on the top are part of a certain category or are related in some way. You need to choose the answer choice that is best associated with the top three words.
Bravery Honesty Kindness
Explanation
The correct answer is (B), loyalty.
Bravery, Honesty, and Kindness are all widely regarded as positive moral qualities (virtues). Loyalty is also usually regarded as a positive moral quality involving commitment and faithfulness.
Why are the rest of the answer choices incorrect?
- Strength can mean both physical power (lifting something heavy) and inner strength (emotional resilience), so it isn’t as clear and specific as the three words in the question which refer to inner qualities. In addition, even when we talk about inner strength, it describes more of a state or capacity (being able to handle hard things) rather than a moral virtue (like kindness or honesty, which are about behaving well).
- Wisdom is a positive quality but relates primarily to judgment and understanding, not directly to moral behavior.
- Speed and Height are just physical traits.
Verbal Analogies
You are presented with two pairs of words. Your goal is:
- To understand how the words in the first pair go together – define the relationship between them.
- Then, choose the word that maintains the same relationship with the first word in the second pair.
dove → peace : scales → ?
Explanation
The correct answer is (A), justice.
A dove is a symbol that stands for peace, just like scales (⚖️) are a symbol that stands for justice.
Why the other choices are incorrect:
- B) weight – Scales can measure weight, but in this question, we are looking for what they represent as a symbol, not what they do.
- C) balance – Balance is related to scales, but balance is more of a state, not an idea the scales stand for.
- D) fairness – Fairness is close to justice, but the scales are most strongly connected to the concept of justice as a system of laws.
If it’s still not quite clear, read the following distinction:
Fairness is about being even and treating people nicely.
Justice is about the official way of deciding what is fair by using laws and rules.
The scales are a symbol especially used in courts and legal systems, where they stand for justice, not just fairness (even though justice should include fairness).
E) measure – This is what scales do (they measure), not what they represent as a symbol.
Quantitative Battery
Number Analogies
Each number analogies question has three pairs of numbers in brackets that follow the same pattern. You need to understand the pattern to find the missing number in the third pair.
[7 → 24] [12 → 39] [13 → ?]
Explanation
The correct answer is (D), 42.
Let’s tackle this analogy step-by-step:
- Look for a pattern:
First, see how the first number changes into the second number in each pair. - Check if multiplying helps in bringing you closer to the second number:
7 × 3 = 21
This is close to 24.
3. Now, check if you need to add something to get to the second number:
21 + 3 = 24
This works!
4. Check the same rule with the second pair:
12 × 3 = 36
36 + 3 = 39
It works again!
Rule found:
Multiply by 3 and then add 3.
5. Apply the rule to 13:
13 × 3 = 39
39 + 3 = 42
Final Answer: 42
Number Series
You are presented with a sequence which follows a certain rule. Identify the rule and then use it to figure out the next number in the sequence.
55 24 51 30 47 36 43 42 ?
Explanation
The correct answer is (C), 39.
Let’s tackle this sequence step-by-step:
1️. Look at how the numbers are arranged:
The numbers switch back and forth:
- 1st, 3rd, 5th, 7th, 9th positions are one pattern.
- 2nd, 4th, 6th, 8th positions are a different pattern.
2️. Check the odd positions:
55 (1s position)
51 (3rd position)
47 (5th position)
43 (7th position)
Notice how each number gets smaller by 4:
- 55 − 4 = 51
- 51 − 4 = 47
- 47 − 4 = 43
So, the next number also goes down by 4:
43 − 4 = 39
3️. Check the even positions to be sure:
24 (2nd position)
30 (4th position)
36 (6th position)
42 (8th position)
Each time the number goes up by 6:
24 + 6 = 30
30 + 6 = 36
36 + 6 = 42
But the missing number in the sequence is in an odd position (9th position), so we only need the rule of subtracting 4 from the number in the 7th position to find it:
43 – 4 = 39
Final Answer: 39
Spatial Reasoning Battery
Figure Analysis
Figure Analysis questions show a folded paper with holes punched in it. Choose the answer that shows how the paper looks when completely unfolded.

Explanation
The correct answer is (E).
First, let’s explain the folding steps in this question:
- The paper has been folded vertically from right to left (panel 2).
- The paper has been folded horizontally from top to bottom (panel 3).
- Two holes have been punched in the folded paper:
- A pentagon-shaped hole. Notice that this hole has been punched right next to the vertical crease.
- A circle-shaped hole to the left of the pentagon-shaped hole.
Second, let’s consider the number of holes that should appear after unfolding the paper:
Two holes have been punched through four layers of paper, so, 2 holes × 4 layers = 8 holes. So we should look for an answer choice with eight holes, shouldn’t we? And the answer is – NO!
As we have mentioned earlier, the pentagon-shaped hole had been punched right next to the vertical crease. It means that when unfolding the paper vertically from left to right, there will be two pentagons whose bases are attached to each other, with no gap in between. Therefore, each of the pentagon-shaped holes will eventually look like one hexagon.
So, it is correct that we should have a total of eight holes, but these holes will look like six holes, because of the four pentagon-shaped holes creating two hexagons. We need to look for an answer with six holes.
You can rule out answer choice (B) as it contains eight holes. In addition, no hexagons can be seen in this answer.
You can also rule out answer choice (D) as it contains only four holes.
Third, let’s unfold the paper:
- Unfold the paper horizontally from bottom to top:

2. Unfold the paper vertically from left to right:

This is exactly answer choice (E)!
Figure Recognition
In this type of questions, you are given a single shape below the answer choices. You need to locate this exact same shape inside one of the structures in the answer choices. Remember – you need to find an identical shape, which means:
- Same size.
- Same direction.
- Same number of edges.
- The edges must look the same.
![]()
Explanation
The correct answer is (A).
The shape you need to locate in this question is an arrow pointing down.
Here is an illustration that will help you see where this shape is in answer (A).
Why are the rest of the answer choices incorrect?
- Answer choice (B) has an arrow pointing down on the left of the figure, but it is cut and incomplete:

- Answer choice (C) has one cut and incomplete arrow pointing down in the middle of the figure. In addition, it has an arrow pointing down on the left of the figure, but this arrow is larger than the original arrow:

- Answer choices (D) and (E) have arrows pointing down, but parts of their edges are missing:
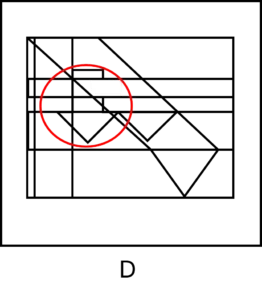
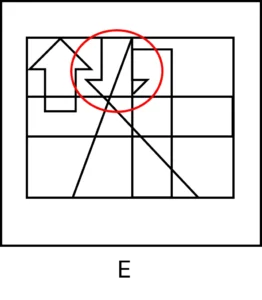
Take home message: this question demonstrates a main characteristic of CAT4 Figure Recognition questions – the shape you need to locate must be identical to the original single shape!
What is CAT4 Level E?
CAT4 Level E is a version of the Cognitive Abilities Test (Fourth Edition) designed specifically for students aged 12 to 13 years old, typically those in Year 8 (England), Grade 7 (US), or S2 (Scotland). The test doesn’t focus on school subjects like math or English, but instead measures a student’s reasoning abilities—how well they think with words, numbers, shapes, and patterns.
The CAT4 isn’t about memorizing facts. Instead, it looks at how students learn, process new information, and solve problems, even if they’ve never seen a question like it before. The goal is to help schools understand a student’s natural strengths and learning potential, so they can support their academic journey in the best possible way.
Unlike tests that reward quick recall or textbook knowledge, CAT4 challenges students to think logically, spot patterns, and use mental strategies—skills that are important for long-term academic success.
Level E marks a shift toward more abstract and flexible thinking. It challenges students to connect ideas, rotate complex shapes in their minds, and understand subtler word meanings or analogies. This is because ages 12-13 mark a significant jump in children’s cognitive abilities.
CAT4 Level E Topics and Format
The CAT4 Level E test is made up of four main reasoning areas (the same as in the other CAT4 levels), each testing a different kind of thinking. These areas are further divided into eight short tests to keep the pace manageable and engaging.
The Four Core Areas:
Verbal Reasoning:
Measures how well students understand relationships between words, spot patterns in language, and make logical decisions based on written information.
Includes: Verbal Classification and Verbal Analogies.
Note that vocabulary at Level E becomes significantly more abstract and metaphorical, relative to earlier CAT4 levels. While earlier levels focus mostly on clear, concrete words (e.g., apple → fruit), Level E includes more abstract concepts, such as:
- Loyalty → virtue
- Predict → forecast
- Generous → selfish (antonym reasoning)
Non-Verbal Reasoning:
Tests the ability to spot patterns and rules using shapes and figures, without any words or numbers involved.
Includes: Figure Classification and Figure Matrices.
Quantitative Reasoning:
Focuses on numerical patterns and logical number problems. This isn’t traditional math but more about how well students spot number-based rules.
Includes: Number Analogies and Number Series.
Note that quantitative reasoning at CAT4 Level E often includes multi-step number rules and alternating patterns, significantly more than in earlier CAT4 levels.
Spatial Ability:
Assesses how well students understand how shapes move, rotate, and fit together in space—a key skill for STEM fields like engineering and design.
Includes: Figure Analysis and Figure Recognition.
Note that In the spatial sections, Level E pushes students to mentally rotate and deconstruct much more complex shapes than in earlier CAT4 levels – this is one of the major challenges Level E brings.
Each part of the CAT4 requires the students to work quickly and accurately, but no prior knowledge is needed—it’s all about how they think and problem-solve.
CAT4 Level E Structure (Timings + No. Questions)
CAT4 Level E consists of eight short tests, typically delivered on a computer or tablet. The test usually takes just under 2 hours in total, including instructions and practice questions.
Here’s a breakdown of the structure:
| Battery (Topic) | Sub-Test | No. of Questions | Time per Sub-Test |
| Part 1 | |||
| Non-verbal | Figure Classification | 24 questions | 10 minutes |
| Figure Matrices | 24 questions | 10 minutes | |
| Part 2 | |||
| Verbal | Verbal Classification | 24 questions | 8 minutes |
| Verbal Analogies | 24 questions | 8 minutes | |
| Quantitative | Number Analogies | 18 questions | 10 minutes |
| Part 3 | |||
| Quantitative | Number Series | 18 questions | 8 minutes |
| Spatial | Figure Analysis | 18 questions | 9 minutes |
| Figure Recognition | 18 questions | 9 minutes | |
| Total | 168 questions | 72 minutes | |
Total testing time: ~72 minutes (not including breaks and setup).
Each sub-test is timed separately, and students must answer as many questions as they can within that time. Instructions and practice examples are given before each section to make sure students know what to expect.
The test structure in Level E is the same as in levels A-D, F, and G.