On this page, you will find a complete breakdown of the CAT4 Level F test for Year 9 and Year 10 students — including what it measures, how it is structured, and the types of reasoning it covers. In addition, you will find free sample questions from each part of the CAT4 Level F test (verbal, non-verbal, quantitative, and spatial), along with a downloadable PDF with these sample questions.
Non-Verbal Battery
Figure Classification
In figure classification questions, you are presented with three figures on the top row that are similar in some way or share a certain characteristic. Then you need to choose the answer choice from the bottom row that also shares this characteristic. Please note that there can be more than one characteristic that binds the three figures in the top row together.
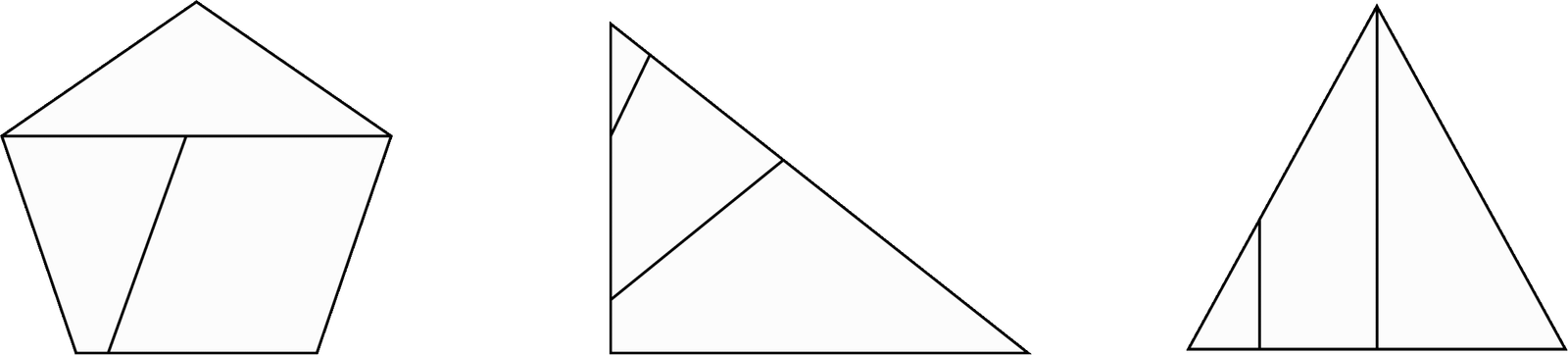
Explanation
The correct answer is (C).
The three figures on the top are similar in the following ways:
- Each figure consists of a shape with an odd number of sides.
- Each shape contains two inner lines, dividing the shape into three unequal parts.
Answer (C) matches these rules:
- The shape is a pentagon and has five sides, which is an odd number.
- The pentagon contains two inner lines, dividing it into three unequal parts.
Figure Matrices
Figure matrices questions on the CAT4 use 2*2 or 3*3 matrices. The figures on the matrices change across the rows from left to right and/or down the columns from top to bottom according to a certain rule. Your goal is to find the rule and apply it to find the missing figure (represented by “?”).
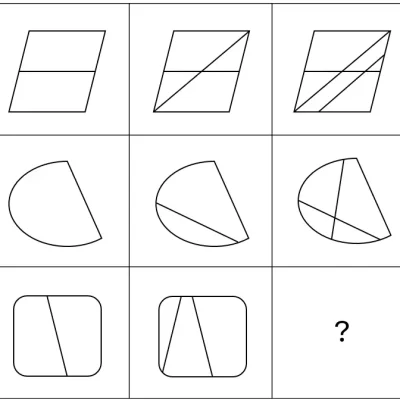
Explanation
The correct answer is (B).
Here you have a 3*3 matrix. The rule, from left to right:
- Each time, one inner diagonal line is added to the figure.
The only answer choice that fits this rule is (B).
Why the rest of the answer choices are incorrect:
- In answer (A) two diagonal lines are added, instead of just one.
- In answer (C), a vertical line is added instead of a diagonal line.
- In answer (D), one line is removed while a line should be added.
- In answer (E), a horizontal line is added instead of a diagonal line.
Verbal Battery
Verbal Classification
The three words on the top are part of a certain category or are related in some way. You need to choose the answer choice that is best associated with the top three words.
painting vase sculpture
Explanation
The correct answer is (D), frame.
Painting, vase, and sculpture are primarily decorative objects that are meant to be looked at and appreciated visually. So is a frame — it is designed to display or enhance visual items (photos, artwork).
Let’s check the distractors:
A) rug – sometimes decorative, but often functional (warmth, sound-dampening, floor protection).
B) chair – primarily functional (sitting).
C) clock – has a visual presence, but it is primarily functional (tells the time).
E) pillow – primarily used for comfort, not for visual display or decoration.
Verbal Analogies
The words in the first pair go together in a certain way. Your goal is to understand how they go together, and then choose the answer choice that goes together with the first word in the second pair in the exact same way.
Compass → direction : microscope → ?
Explanation
The correct answer is (D), detail.
This is a tool-to-purpose relationship:
- A compass is a tool used to find direction.
- A microscope is a tool used to see small details.
So the relationship is:
Tool → what it helps you detect
Let’s see why the other answer choices are incorrect:
A) lens – lenses are an essential part of a microscope, but you do not use the microscope to find lenses.
B) biology – while microscopes are used in biology, you don’t “see biology” itself — it’s too broad. You use a microscope to observe specific details within biology, like cells or bacteria.
C) vision – microscopes help you see things that are too small to see unaided, so “vision” is too general to fit this analogy.
E) observation – this describes an action, not an outcome. A microscope helps you observe, but more precisely, it helps you observe fine details — which is why “detail” is the better fit.
Quantitative Battery
Number Analogies
Each number analogies question has three pairs of numbers in brackets that follow the same pattern. You need to understand the pattern to find the missing number in the third pair.
[36 → 10] [48 → 14] [30 → ?]
Explanation
The correct answer is (A), 8.
Let’s test this 2-step rule:
Divide by 3, then subtract 2
- 36 ÷ 3 = 12, then 12 − 2 = 10
- 48 ÷ 3 = 16, then 16 − 2 = 14
- 30 ÷ 3 = 10, then 10 − 2 = 8
Tip: Looking for an arithmetic operation that brings the first number closer to the second number is many times the key in CAT4 number analogies. So, if you are stuck, try to bring the first number closer to the second number by either addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division, and then see what is the next arithmetic operation that you need to apply.
Number Series
You are presented with a sequence which follows a certain rule. Identify the rule and then use it to figure out the next number in the sequence.
3 6 12 4 8 16 5 10 ?
Explanation
The correct answer is (D), 20.
Let’s break the solution into steps:
Step 1: Group the numbers into threes
Look at the sequence in sets of 3:
- Group 1: 3, 6, 12
- Group 2: 4, 8, 16
- Group 3: 5, 10, ?
Step 2: Find the pattern within each group
In each group, the numbers follow this rule:
Start × 2 → middle, middle × 2 → last
- Group 1:
3 → 6 → 12
(3 × 2 = 6, 6 × 2 = 12) - Group 2:
4 → 8 → 16
(4 × 2 = 8, 8 × 2 = 16) - Group 3:
5 → 10 → ?
(5 × 2 = 10, 10 × 2 = 20)
Step 3: Notice the starting numbers of each group
- First group starts at 3
- Second group starts at 4
- Third group starts at 5
So, the starting number increases by 1 with each group.
Summary:
Each group of 3 numbers:
- Starts with a number that increases by 1 each time (3 → 4 → 5)
- Then doubles:
Start × 2 → middle
Middle × 2 → end
So the missing number is 10 × 2 = 20.
Spatial Reasoning Battery
Figure Analysis
Figure Analysis questions show a folded paper with holes punched in it. Choose the answer that shows how the paper looks when completely unfolded.
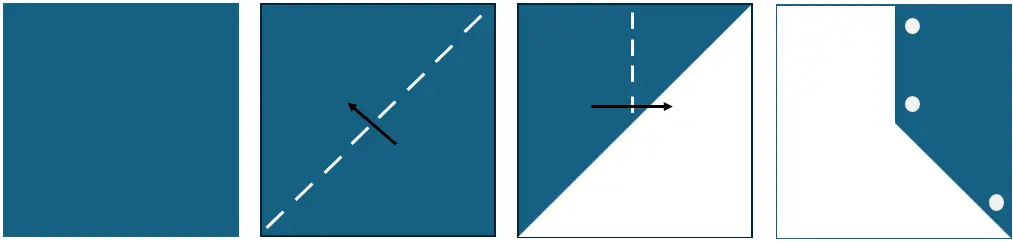
Explanation
The correct answer is (E).
First, let’s explain the folding steps in this question:
- The paper has been folded diagonally from the bottom-right corner to the top-left corner (panel 2).
- The paper has been folded vertically from left to right (panel 3).
- Three holes have been punched in the folded paper.
Second, let’s consider the number of holes that should appear after unfolding the paper:
- The hole at the bottom of the figure has been punched through two layers of paper. Therefore, after unfolding the paper, this hole will become two holes (1 * 2 = 2).
- The two holes at the top of the figure have been punched through four layers of paper. Therefore, after unfolding the paper, these two holes will become eight holes (2 * 4 = 8).
- In total, there should be 10 holes after unfolding the paper (2 + 8 = 10).
- Answer choices (C) and (D) can be ruled out as they contain 8 and 12 holes, respectively.
Answer choice (A) is incorrect as the holes at the bottom left side should be closer to the bottom left corner.
Answer choice (B) is incorrect as the holes on the right should be closer to each other and to the right edge of the figure.
Figure Recognition
In this type of questions, you are given a single shape below the answer choices. You need to locate this exact same shape inside one of the structures in the answer choices. Remember – you need to find an identical shape, which means:
- Same size.
- Same direction.
- Same number of edges.
- The edges must look the same.
![]()
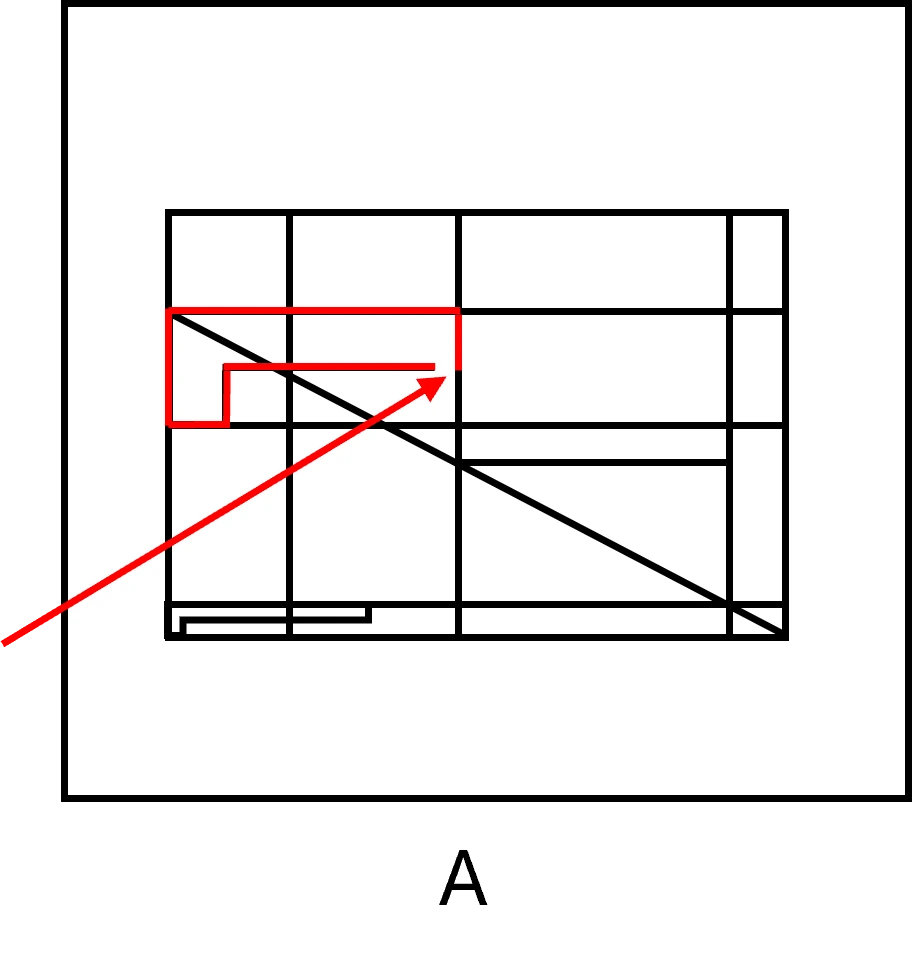
Explanation
The correct answer is (B).
The shape you need to locate is an L-shape rotated 90 degrees clockwise.
The following illustration will help you see where this shape is located in answer (B) – click here.
Why are the rest of the answer choices incorrect? There are L-shapes in all of the answer choices, but they are either smaller or bigger than the original L-shape. Alternatively, they are positioned in a different direction compared to the original L-shape.
Only answer choice (A) is a bit different – let’s check it and see why it is incorrect:
- There is an incomplete L-shape in this answer choice – its edge on the right is incomplete:
What is CAT4 Level F?
CAT4 Level F is part of the Cognitive Abilities Test (CAT4) series and is typically taken by students in Year 9 or Year 10, around ages 13 to 15. Like the other CAT4 levels, it doesn’t test what students have learned in school, but instead measures how they think, solve problems, and process information in different ways — with words, numbers, shapes, and spatial patterns.
So what is unique about CAT4 level F?
1. Target age group:
CAT4 Level F is typically taken by students in Year 9 or Year 10 (ages 13–15). This places them at a transitional academic stage, where schools often make important decisions about subject pathways (e.g., GCSE choices, tracked courses, or support needs).
2. Used for early future planning:
Because students at this age are approaching more specialized learning, Level F data can inform decisions about:
- Course selection (STEM vs. humanities)
- Advanced placement or intervention needs
3. One level below CAT4 Level G:
Level F is the second-highest level in the CAT4 series. Students who are performing above expected levels may later sit Level G in Year 11+ — making Level F useful for identifying students on the cusp of higher-level thinking.
CAT4 Level F Topics and Format
CAT4 Level F includes the same four reasoning areas as other levels in the CAT4 series: Verbal, Non-Verbal, Quantitative, and Spatial. Each area is tested through two short sub-tests, making a total of eight sub-tests overall.
- Verbal Reasoning checks how well students understand language and identify logical relationships between words.
- Non-Verbal Reasoning involves solving visual problems using shapes and patterns, without relying on language.
- Quantitative Reasoning focuses on number patterns, rules, and abstract number logic.
- Spatial Ability assesses how well students can visualize and mentally manipulate shapes — a key skill in design, engineering, and science.
All questions are multiple-choice with five answer options. The test is available in both digital and paper format, and typically takes around two hours, including breaks between parts.
CAT4 Level F Structure (Timings + No. Questions)
The CAT4 Level F follows the same format and structure used across all standard CAT4 levels. It includes a set of eight short sub-tests, grouped under four key reasoning areas. The table below outlines the structure of the test — including each sub-test, the number of questions, and the time allowed. While the actual testing time adds up to 72 minutes, the full session usually takes about two hours once instructions, setup, and short breaks are included. The test is typically administered in separate parts, with pauses between sections to help students stay focused.
| Battery (Topic) | Sub-Test | No. of Questions | Time per Sub-Test |
| Part 1 | |||
| Non-verbal | Figure Classification | 24 questions | 10 minutes |
| Figure Matrices | 24 questions | 10 minutes | |
| Part 2 | |||
| Verbal | Verbal Classification | 24 questions | 8 minutes |
| Verbal Analogies | 24 questions | 8 minutes | |
| Quantitative | Number Analogies | 18 questions | 10 minutes |
| Part 3 | |||
| Quantitative | Number Series | 18 questions | 8 minutes |
| Spatial | Figure Analysis | 18 questions | 9 minutes |
| Figure Recognition | 18 questions | 9 minutes | |
| Total | 168 questions | 72 minutes | |
