This page provides sample questions of the CAT4 Level G test (Year 11+). The sample questions are from each part of the test: non-verbal, verbal, quantitative, and spatial reasoning. You can practice interactively on the page, or download a PDF version of these questions. In addition, this page includes a clear guide about the CAT4 Level G test format, what skills it assesses, and how the test is structured.
Non-Verbal Battery
Figure Classification
In figure classification questions, you are presented with three figures on the top row that are similar in some way or share a certain characteristic. Then you need to choose the answer choice from the bottom row that also shares this characteristic. Please note that there can be more than one characteristic that binds the three figures in the top row together.
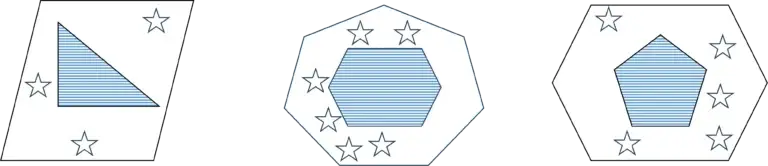
Explanation
The correct answer is (A).
The three figures on the top are similar in the following ways:
- Each figure consists of a small shape inside a larger shape. The larger shape has one more side than the smaller shape.
- The smaller shape is filled with horizontal lines.
- Stars are located between the larger shape and the smaller shape. The number of stars = the number of sides of the smaller shape.
Answer (A) matches these rules:
- The larger shape has five sides (a pentagon).
- The smaller shape has four sides (a square), and is filled with horizontal lines.
- There are four stars between the larger shape and the smaller shape, which is the number of sides of the smaller shape (a square).
Figure Matrices
Figure matrices questions on the CAT4 use 2*2 or 3*3 matrices. The figures on the matrices change across the rows from left to right and/or down the columns from top to bottom according to a certain rule. Your goal is to find the rule and apply it to find the missing figure (represented by “?”).
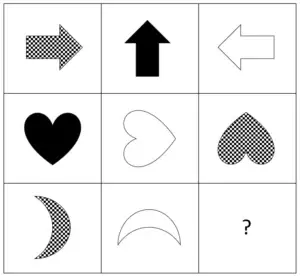
Explanation
The correct answer is (E).
Here you have a 3*3 matrix. You can see there are two rules/patterns here:
- From left to right, the figures rotate 90 degrees counterclockwise each time.
- In each row, there are three types of fillings: checkered, white, and black. Each type of filling appears once.
As in the third row there are already checkered and white figures, the next figure must be black. So you can rule out answer choices (B) and (D).
Answer (A) can be ruled out as it is the middle figure in the third row rotated 180 degrees and not 90 as needed.
Answer (C) can be ruled out as it is the middle figure in the third row rotated 90 degrees clockwise and not counterclockwise as needed.
Verbal Battery
Verbal Classification
The three words on the top are part of a certain category or are related in some way. You need to choose the answer choice that is best associated with the top three words.
carpenter painter bricklayer
Explanation
The correct answer is (B), roofer.
Carpenter, painter, and bricklayer are all manual, skilled trades in the construction industry. They involve hands-on work and are considered specific professions. Roofer is the only option that fits this group — it is also a skilled trade in construction.
Why the other options are incorrect:
(A) mechanic – A skilled trade, but related to vehicles, not buildings.
(C) builder – Too general, as it does not refer to a specific trade. For example, you can say that carpenters, painters, and bricklayers are all types of builders.
(D) construction – Refers to an industry or field, not a profession or job role.
(E) engineer – Often works in building design, but it is an academic/professional role, not a manual trade.
Verbal Analogies
You are presented with two pairs of words. Your goal is:
- To understand how the words in the first pair go together – define the relationship between them.
- Then, choose the word that maintains the same relationship with the first word in the second pair.
Curiosity → discovery : doubt →
Explanation
The correct answer is (C), Understanding.
- Curiosity → Discovery: Curiosity is a mental state that motivates a process that in turn leads to knowledge (discovery).
- Doubt → Understanding: Doubt is a mental state that motivates a process -investigation, that in turn leads to clarity or insight (understanding).
Both pairs follow a pattern of internal state → process → knowledge-based outcome.
Why the other choices are incorrect:
A) Ignorance
- Ignorance is not a result of doubt — if anything, doubt helps challenge or resolve ignorance.
- The direction of the relationship doesn’t match.
B) Fear
- Doubt can lead to fear in some contexts, but fear is an emotional reaction, not a cognitive outcome. In addition, fear, if it happens, is a direct by-product of doubt, but it is not an outcome of the process that doubt leads to.
D) Hesitation
- Hesitation is a momentary pause or delay caused by doubt.
- It doesn’t reflect the end result of engaging with doubt — just a possible side effect.
E) Inquiry
- Inquiry is the process that may result from doubt — just like questioning might follow curiosity.
- But the analogy requires the outcome, not the intermediate step.
Quantitative Battery
Number Analogies
Each number analogies question has three pairs of numbers in brackets that follow the same pattern. You need to understand the pattern to find the missing number in the third pair.
[78 → 20] [54 →12] [51→ ?]
Explanation
The correct answer is (B), 11.
At first, simple subtraction doesn’t help — the gaps between the numbers (like 78 → 20 or 54 → 12) aren’t the same. That suggests we need a multi-step rule.
When one number is much smaller than the other, it’s helpful to look for a division step that brings you closer.
Try dividing by 3:
- 78 ÷ 3 = 26 → 26 is already pretty close to 20. To get from 26 to 20 you need to subtract 6:
26 − 6 = 20 - Now apply this rule to the second pair:
54 ÷ 3 = 18
18 − 6 = 12
It works! So the rule is first to divide by 3, and then subtract by 6. - Apply it to the third pair:
51 ÷ 3 = 17
17 − 6 = 11
11 is the correct answer!
Take-home message: Looking for an arithmetic operation (such as dividing) that reduces the first number and brings it closer to the second number is many times the key in CAT4 number analogies.
Number Series
You are presented with a sequence which follows a certain rule. Identify the rule and then use it to figure out the next number in the sequence.
48 45 40 38 32 ?
Explanation
The correct answer is (D), 31.
This is an alternating two-pattern sequence:

- On odd-numbered positions (1st, 3rd, 5th), the decrease to the next number is getting 1 smaller each time:
(−3 ➔ −2 ➔ −1) - On even-numbered positions (2nd, 4th, 6th), the decrease to the next number is getting 1 larger each time:
(−5 ➔ −6 ➔ −7)
The last number in the series is 32, and it is located in the 5th position = odd position. The last move from an odd position was -2 (from 40 to 38). As each time the moves from the odd positions to the next number decrease by one, you now need to subtract -1 from 32 to get 31.
Spatial Reasoning Battery
Figure Analysis
Figure Analysis questions show a folded paper with holes punched in it. Choose the answer that shows how the paper looks when completely unfolded.
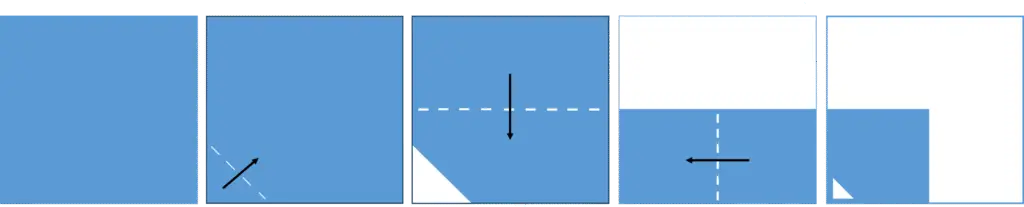
Explanation
The correct answer is (C).
First, let’s explain the folding steps in this question:
- The bottom-left corner of the paper has been folded diagonally (panel 2), leaving this corner empty (panel 3).
- The upper half of the paper has been folded horizontally (panel 3). As a result, now the empty corner seen in panel 3 is covered by one layer of paper (panel 4).
- The right half of the paper has been folded vertically (panel 4). As a result, now the bottom left corner is covered by another two layers of paper, making it a total of three layers of paper.
- A triangle-shaped hole has been punched at the bottom left corner (panel 5).
Second, as we know that the triangle-shaped hole has been punched through three layers of paper, the total number of holes after unfolding the paper would be 1 * 3 = 3 triangle-shaped holes. Therefore, answer choice (D) can be ruled out, as it contains four holes.
Third, let’s unfold the paper:



It perfectly matches answer choice (C)!
Why is answer choice (A) incorrect? Indeed, the holes in answer (A) are located at the correct places, but their direction is incorrect. Why is that? Because when we fold along a symmetry line, the points of the shapes from both sides of the line must have the same distance from the line, hence mirroring each other. For example:
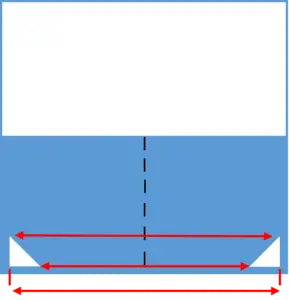
Therefore, only answer choice (C) shows the triangle-shape holes in both the correct location and correct direction.
Figure Recognition
In this type of questions, you are given a single shape below the answer choices. You need to locate this exact same shape inside one of the structures in the answer choices. Remember – you need to find an identical shape, which means:
- Same size.
- Same direction.
- Same number of edges.
- The edges must look the same.
![]()
Explanation
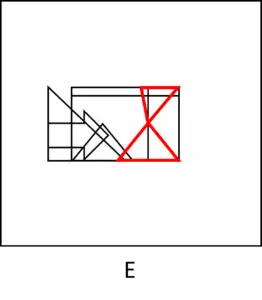
The correct answer is (D).
The shape you need to locate is built from two opposite isosceles triangles mirroring each other, with a lower triangle and an upper triangle.
The following illustration will help you see where this shape is located in answer (D):
Figure Recognition Illustration – Click Here
Be careful of the distractors – they are meant to mislead you! Let’s rule out the rest of the answer choices together:
Answer (A): there are two opposite triangles in the same way as in the original single shape. However, the base of the upper triangle is incomplete, making this answer incorrect: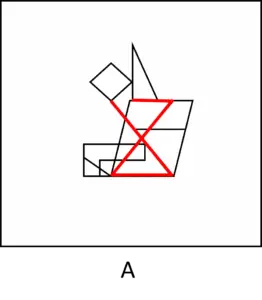
Answer (B): The single shape does appear – but in a different direction (slanted left) than the original single shape (not slanted) – making it an incorrect answer: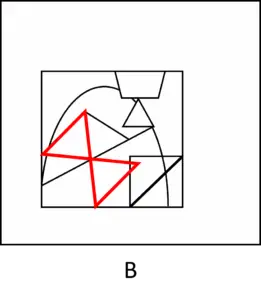
Answer (C): The single shape appears twice – but in the wrong size, way too smaller than the original single shape. In addition, one of the shapes also appears in the wrong direction, with the triangles located next to one another and not on top of each other: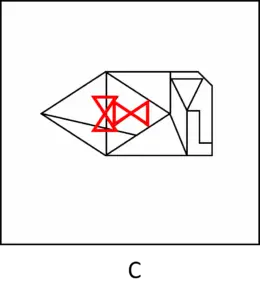
Answer (E): You may have noticed that there is a shape built from two opposite triangles on the right of the figure. But if you look closely – you can see that the shape is not identical to the original single shape – the upper triangle looks different from the upper triangle in the original single shape.
What Does CAT4 Level G Mean?
CAT4 Level G (Year 11+) refers to the most advanced level of the Cognitive Abilities Test (CAT4), designed for students aged 15 years and above, typically in Year 11 or higher. It assesses a student’s ability to reason with words, numbers, shapes, and spatial patterns — not what they’ve learned in school, but how they think and solve problems. The “G” simply indicates the highest level in the CAT4 series, with earlier levels (A–F, X, Y, and Pre-A) tailored to younger age groups. Level G is often used for older students in secondary school or international settings, especially when making decisions about academic support, future pathways, or placement.
While Level G may seem harder than earlier levels, it isn’t necessarily harder — it’s simply matched to the developmental stage of older students. The tasks in it are designed to reflect how teens at this age typically think and reason, not to be more challenging just for the sake of difficulty.
Like all CAT4 levels, Level G is not based on any curriculum — it measures reasoning skills that underlie academic performance, regardless of subjects studied.
CAT4 Level G Topics and Format
CAT4 Level G uses the same four batteries as all other CAT4 levels (A–F), each targeting a different area of reasoning:
- Verbal Reasoning assesses how well students understand language and spot logical relationships between words.
- Non-Verbal Reasoning focuses on recognizing patterns and solving problems using shapes and visuals, with no reading required.
- Quantitative Reasoning looks at number-based logic, especially patterns and sequences.
- Spatial Ability measures how accurately students can imagine and manipulate objects in space — a skill useful in technical and design-related subjects.
Each battery contains two brief sub-tests, for a total of eight short sub-tests. The full test takes about two hours, with breaks between parts. The CAT4 Level G format is the same as in the earlier levels – all questions are multiple-choice, with five answer choices and only one correct answer among them. CAT4 Level G is available in both digital and paper format.
CAT4 Level G Structure (Timings + No. Questions)
| Battery (Topic) | Sub-Test | No. of Questions | Time per Sub-Test |
| Part 1 | |||
| Non-verbal | Figure Classification | 24 questions | 10 minutes |
| Figure Matrices | 24 questions | 10 minutes | |
| Part 2 | |||
| Verbal | Verbal Classification | 24 questions | 8 minutes |
| Verbal Analogies | 24 questions | 8 minutes | |
| Quantitative | Number Analogies | 18 questions | 10 minutes |
| Part 3 | |||
| Quantitative | Number Series | 18 questions | 8 minutes |
| Spatial | Figure Analysis | 18 questions | 9 minutes |
| Figure Recognition | 18 questions | 9 minutes | |
| Total | 168 questions | 72 minutes | |
